6 Facts That You Should Know About Testicular Cancer
6 Facts That You Should Know About Testicular Cancer
Testicular Cancer : An Introduction
Testicular cancer is the second most common cancer in young men. Mostly testicular cancer is observed in men ages above 30. Now a days percentage of testicular cancer is increasing. It symptoms of testicular cancer includes painless swelling or lump in testicles. The American Cancer Society reports that about one of every 250 males develops testicular cancer during his lifetime, which makes it somewhat uncommon. Testicular cancer occurs in men at very young age, therefore it is very important to diagnose it at right time.
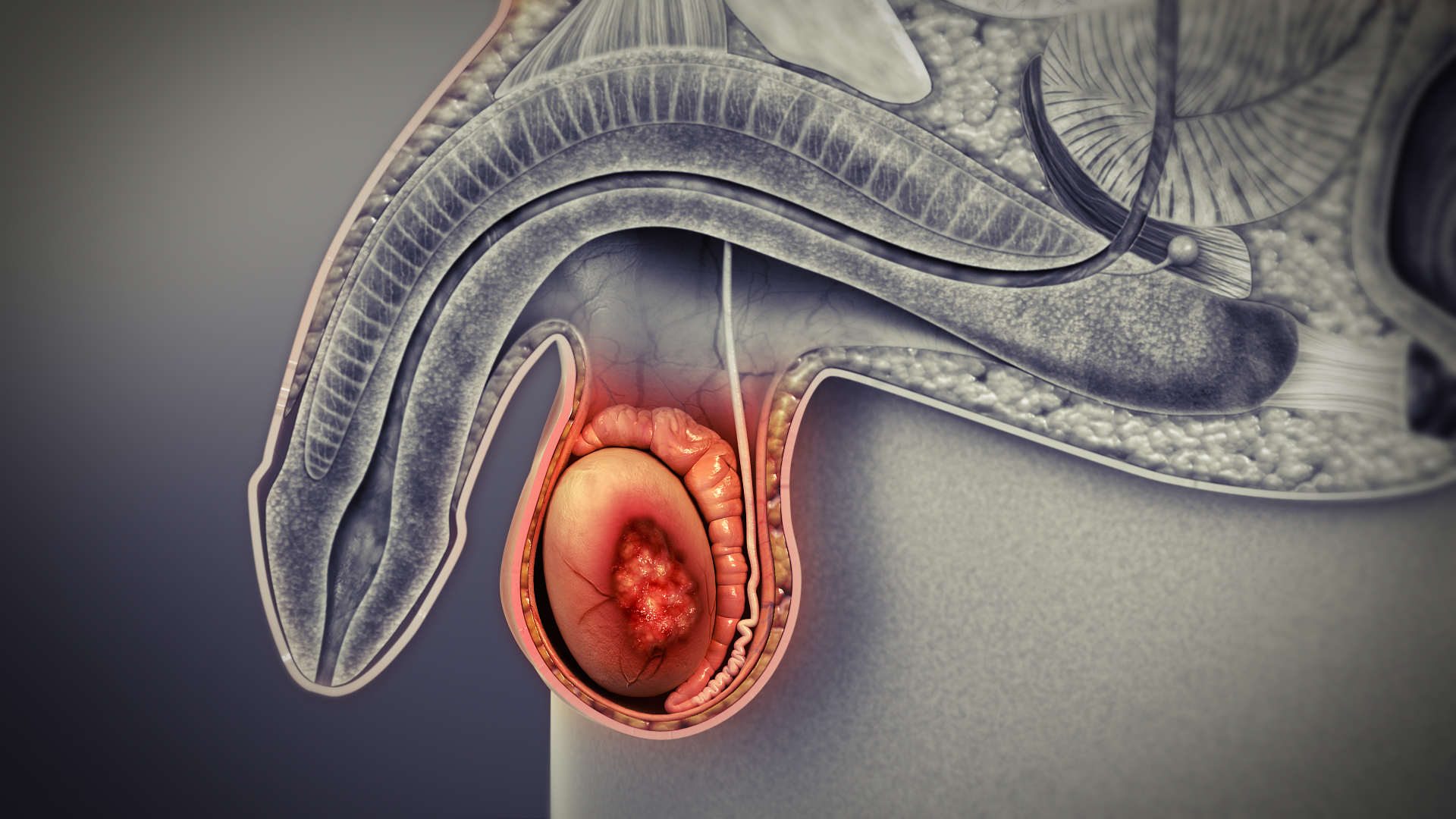
Following are 6 common testicular cancer facts that will help you to better understand the disease and the male body.
Fact 1: Testicular cancer is commonly develop in young and middle-aged men. It has been observed that 8% men are older than 55 yrs.
Fact 2: As it occurs in young males, education including how to perform self-examination should start early. It will reduce risk of developing cancer.
Fact 3: Mostly testicular cancers develop in reproductive cells (that produce sperms). There are two types of germ cell cancers: seminomas and non-seminomas. Seminomas cancers grow slowly as compare to Non-seminomas cancers.
Fact 4: The testicles can host a lot of other growths that are not cancerous. Among them are hydroceles (fluid-filled sacs), varicoceles (enlarged veins in the scrotum) and spermatoceles (painless cysts in the epididymis).
Fact 5: Testicular cancer tends to occur in just one testicle, which can be removed by proper treatment. The removal of a testicle will not affect the ability to have an erection, though it can diminish fertility. However, the other testicle can still be able to produce enough hormones to support a healthy sex life.
Fact 6: If testicular cancer is detected early, patient can recover to great extent. He can live healthy life after proper treatment. The lifetime risk of dying from this cancer is only about 1 in 5,000, because treatment is so effective.

How to Perform a Self-Exam For Testicular Cancer
The risk factors of testicular cancer includes family history, one or two undescended testicles, and Klinefelter syndrome (a genetic disorder that causes low testosterone levels).
Self-exams should be performed monthly even if there are no symptoms present. It just requires shower and two hands. Here’s the procedure for how to perform self test:
- Using both hands, cup one testicle at a time.
- With a slight bit of pressure, roll the testicle between the thumb and fingers. You should familiar with the cords and tubes at the back of the testicles to know the landscape.
- Observe for lumps, irregularities or a change in size.
If you observe any irregularities or lumps are noticed contact immediately with best urologist near you. He can diagnose and suggest you necessary treatment. If cancer is detected in early stage, it can be completely cured. Don’t hesitate to talk about your problems with doctor.
